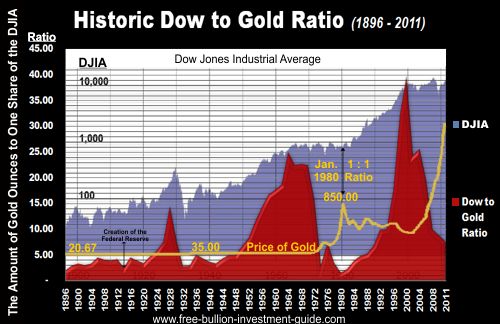
Homepage / Bullion Market Basics: Silver S & D 2011- 2019
Updated 02/15/2024
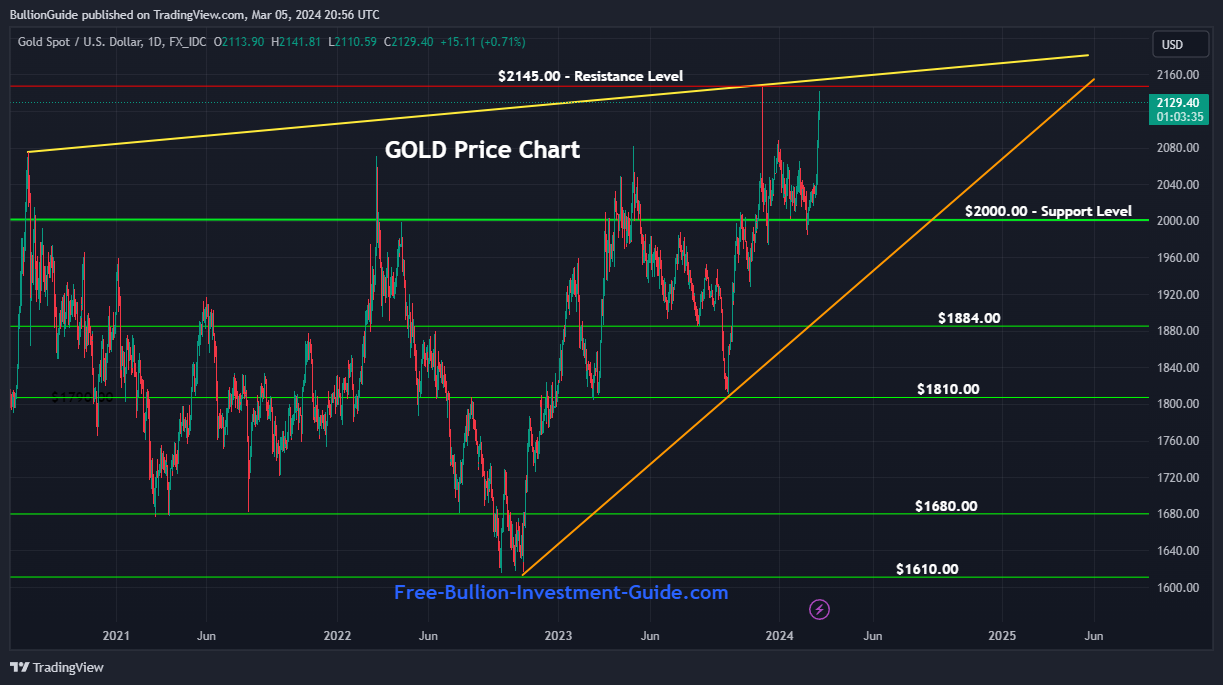
Silver
Supply and Demand
2011 - 2019
Silver Facts
Silver is a metallic chemical element with the chemical symbol Ag; its atomic number is 47. Its symbol comes from the Latin word "Argentum," from the Indo-European root arg- for "grey" or "shining."
 Silver Ore
Silver Ore photo provided courtesy of Wikipedia
Silver has the highest electrical and thermal conductivity of any metal.
Silver is found in the Earth's crust in the pure, free elemental form, as an alloy with gold and other metals, and in minerals such as argentite and chlorargyrite.
Outside of Mexico, silver is seldom mined alone; most silver is mined as a byproduct of copper, gold, lead, and zinc refining.
Silver is part of a small group of elements called precious metals, which include gold and platinum-group metals (PGMs).
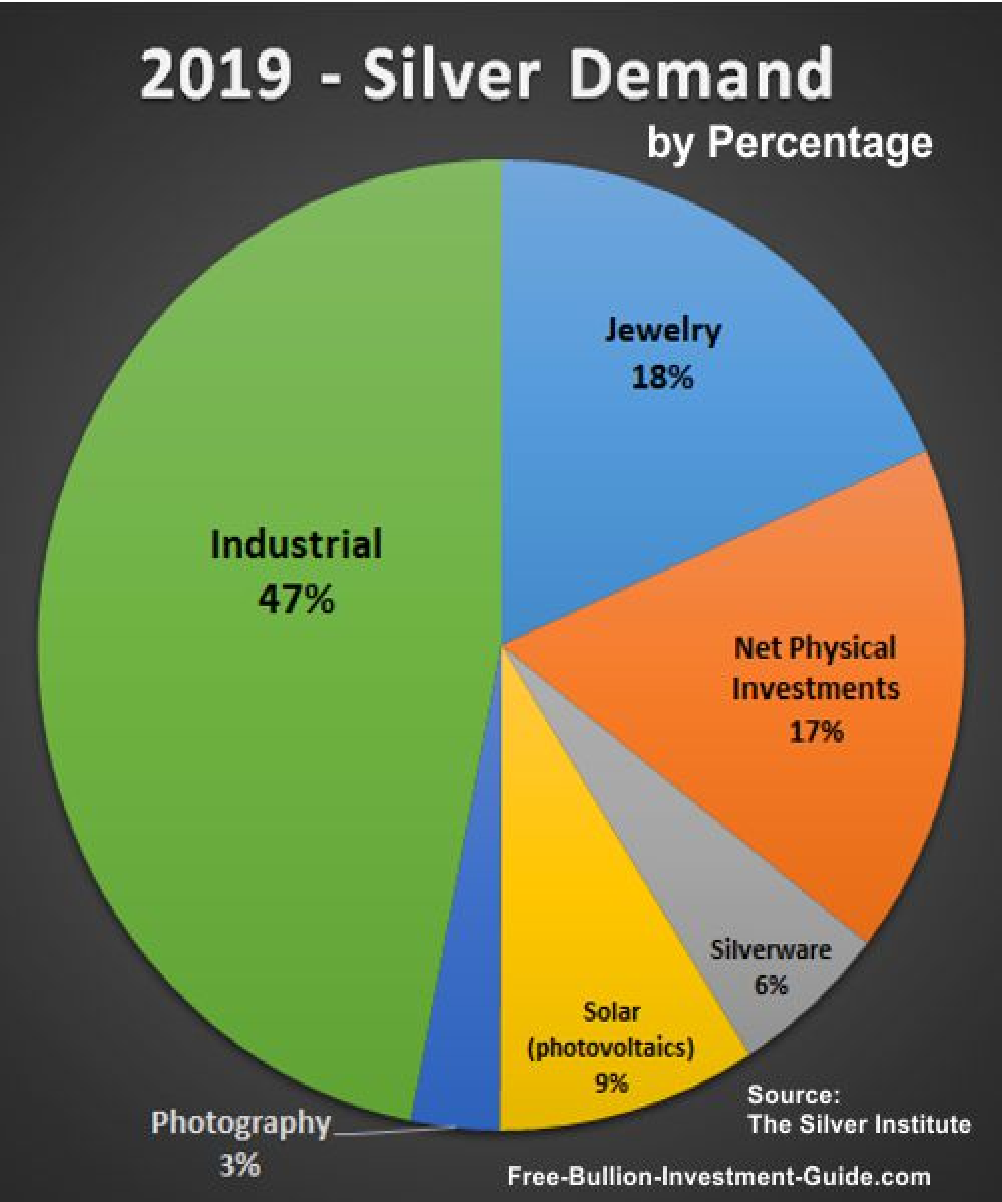
60% of Silver's demand is used in photography, electrical contacts and conductors, in batteries, in the manufacturing of solar panels, and catalysis of chemical reactions. Medically, silver compounds are used as disinfectants and medical antimicrobials.
40% of Silver's demand is in jewelry, high-value tableware, ornaments, utensils, coins, and investment-grade bullion production.
Silver Supply and Demand 2011-2019
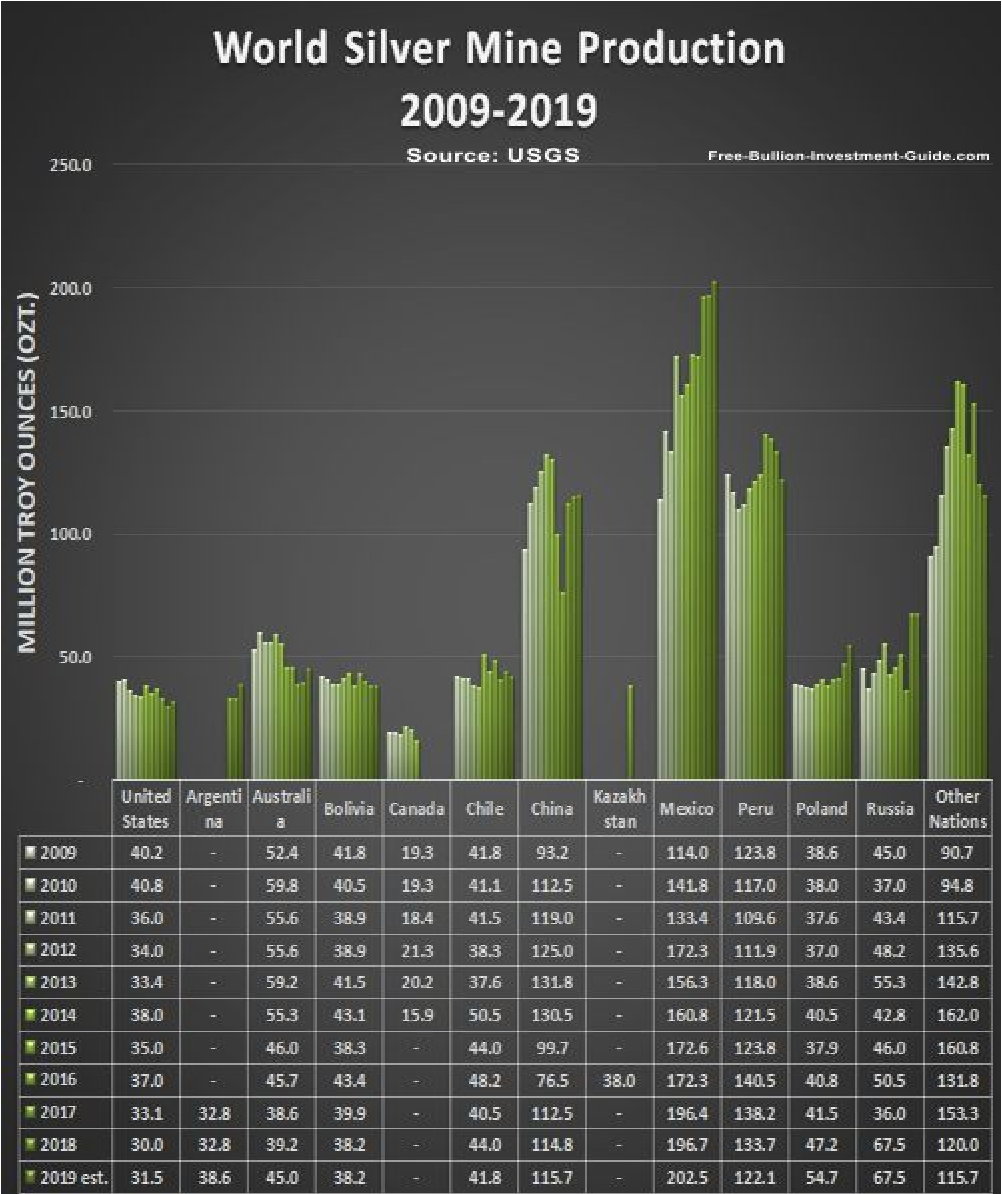
Silver Mine Production
Most global silver mines are poly-metallic ore mines, with over two-thirds being silver-rich deposits containing gold, lead, zinc, and copper.
Silver Supply and Demand 2011 - 2019

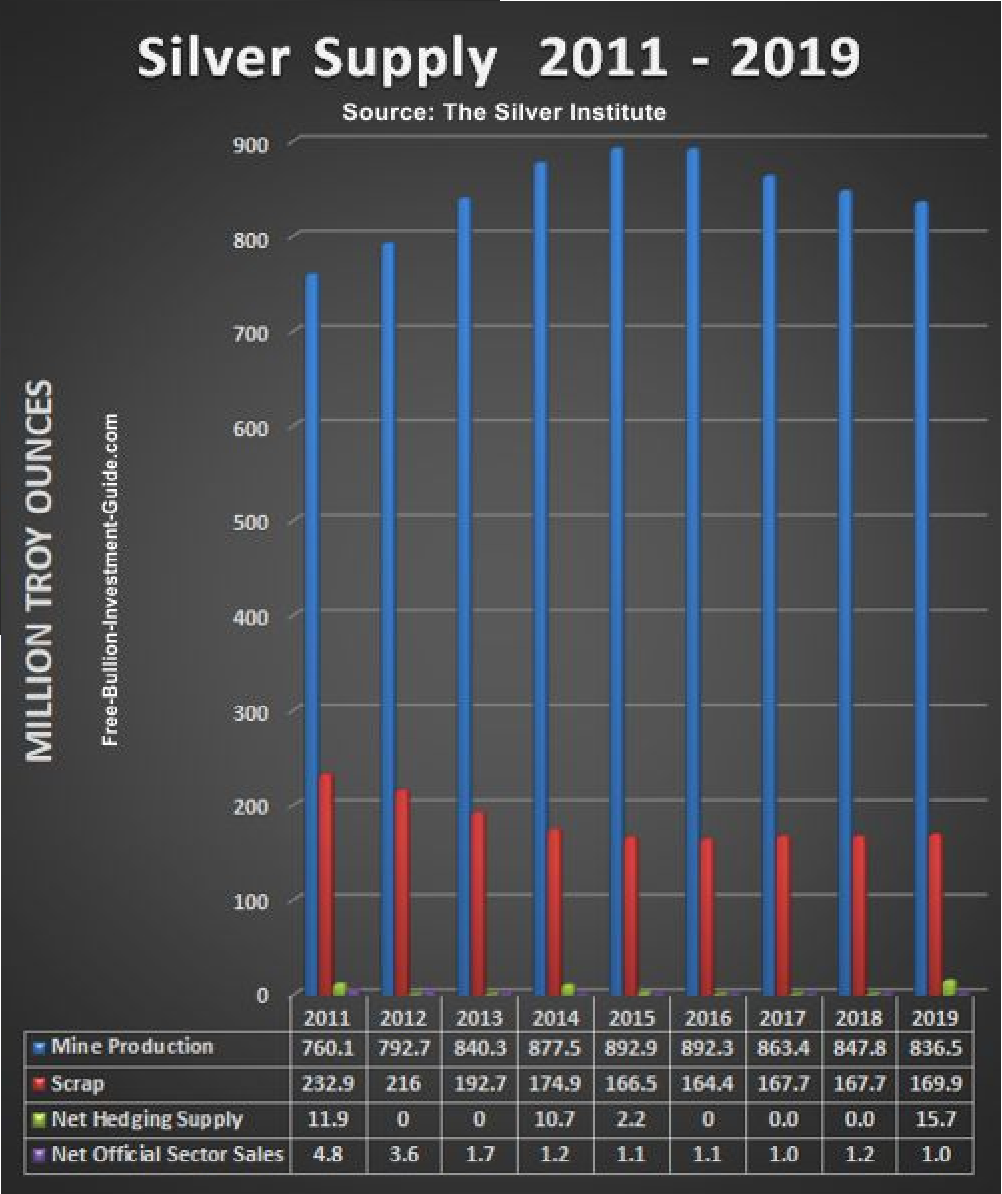
Silver Supply
Scrap Silver
Scrap is the silver that returns to the market
when recovered from manufactured goods.
Producer Hedging
Producer hedging is the early sale of silver ore by mining companies for future production. Hedging may also not appear every year on the supply side on a net basis, as it can form part of demand as de-hedging.
Net Government Sales
Disinvestment and government sales are similar in that both comprise the return to the market of old bars and coins by the private sector and governments. It is worth bearing in mind that these sources may not add to the supply every year on a net basis.
Silver Supply and Demand 2011-2019
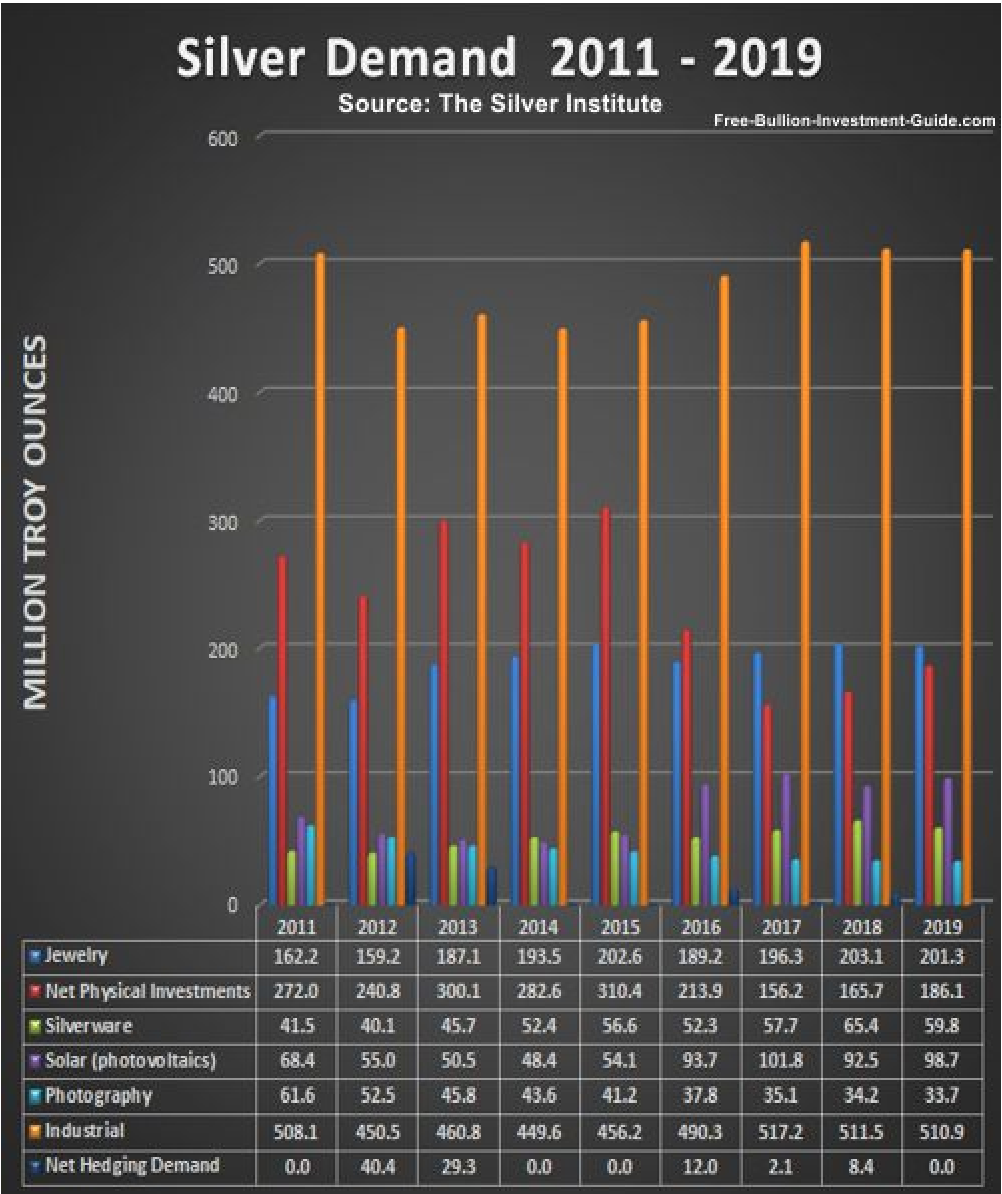
Silver
Demand
Silver Supply and Demand 2011- 2019
Industrial Uses
of Silver
Jewellery
Silver jewelry is prized for its brilliant luster and ease of fabrication. Pure silver has a fineness of .999 or higher; it is too soft for use in jewelry.
Silversmiths often alloy silver with other metals, such as copper, to harden it. Sterling silver, for example, is 92.5 percent silver and 7.5 percent copper. Sterling silver is the standard in many countries for silver jewelry.
Silverware
The same properties that make silver ideal for jewelry also cross over into silverware with its reflectiveness and tarnish resistance. Copper is mixed with silver to toughen it for use as cutlery, bowls and decorative items such as picture frames.
Photography
Silver-based photography happens when light strikes sensitive silver-halide crystals suspended on film. In a chemical process, the differences in light form negative images, which are transferred to paper pictures using silver-embedded paper.
Roughly 5,000 color photographs can be taken using one ounce of silver. The growth of digital photography has caused the use of silver-based imaging by consumers to drop over the past decade.
Nevertheless, because silver-halide film is extremely accurate and cost-effective, it is still favored for some applications.
For example, medical X-ray technicians, especially those in developing countries, prefer silver-based pictures because of their low cost and high accuracy.
In addition, many motion picture makers still prefer silver-halide film over digital because of its low cost, excellent resolution, and true color properties.
Batteries
Many rechargeable and disposable batteries are manufactured with silver alloys as the cathode or negative (-) side.
Although expensive, silver cells have power-to-weight characteristics superior to those of their competitors. The most common of these batteries is the small button-shaped silver oxide cell used in cameras, toys, hearing aids, watches, and calculators.
Due to environmental and safety concerns, silver-oxide batteries are beginning to replace lithium-ion batteries in mobile phones and laptop computers. Silver-zinc batteries feature a water-based chemistry and contain no lithium or flammable liquids.
Bearings
Steel ball bearings electroplated with silver have greater fatigue strength and load-carrying capacity than any other type.
Because steel has poor friction properties, placing a layer of silver between the steel ball bearing and the housing reduces friction, increasing the performance and reliability of the engine.
Electroplated silver bearings are used continuously in heavy-duty applications such as jet engines.
Brazing and Soldering
Silver facilitates the joining of materials, called brazing when done at temperatures above 600 degrees Celsius and soldering when below, and produces naturally smooth, leak-tight, and corrosion-resistant joints.
Silver brazing alloys are utilized in various industries, such as air conditioning, refrigeration, electric power distribution, automobiles, and aerospace.
Silver brazes and solders combine high tensile strength, ductility, and thermal conductivity. Silver-tin solders are used for bonding copper pipe in homes, where they not only eliminate the use of harmful lead-based solders but also provide the piping with silver’s natural antibacterial action.
Major faucet manufacturers also use silver-based bonding materials to incorporate these advantages. Refrigerator manufacturers use silver-based bonding materials to provide the ductility required for constant changes in the temperature of the cooling tubes.
Due to health concerns, the traditional 63 percent tin/37 percent lead solder used to build electronic equipment is quickly being replaced by a combination of silver, tin, and copper solder.
The movement was boosted by the Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) legislation that applies throughout the European Union (EU). The law bans all products containing more than a trace amount of lead, mercury, cadmium, and several other hazardous substances.
Although the laws apply only to EU countries, they are being felt worldwide as companies move to a safer supplier.
Catalysts
A catalyst is a substance that facilitates a chemical process without itself undergoing any transformation because of its unique chemical properties.
More than 150 million ounces of silver annually are catalyst in the world's chemical industry for the production of two major industrial compounds, ethylene oxide and formaldehyde, which are essential to the plastics industry.
Ethylene oxide is the foundation for flexible plastics, such as polyester textiles, used to make all types of clothing. It is also used for molded items such as insulating handles for stoves, keyboards for computers, electrical control knobs, domestic appliance components, and electrical connector housings.
Furthermore, about 25 percent of ethylene oxide production is used for producing antifreeze coolants for automobiles and other vehicles.
Formaldehyde, a chemical produced from methanol, is the building block of solid plastics, including adhesives, laminating resins for construction plywood, and particle boards.
Electronics
Silver has excellent electrical conductivity and is used in many applications in electronics, from printed circuit boards to switches and TV screens.
Silver membrane switches, which require only a light touch, are used in buttons on televisions, telephones, microwave ovens, toys, and computer keyboards.
Silver-based inks and films are used for printed circuit boards, which are used in consumer items ranging from mobile phones to computers to composite boards to create electrical pathways.
Silver-based inks are used to produce RFID tags (radio frequency identification) antennas used in hundreds of millions of products to prevent theft and allow easy inventory control.
Silver is used in the manufacturing process of plasma display panels used in television sets and monitors.
Medical
Silver’s anti-bacterial powers have been tested and proven scientifically, even though its power as a bactericide has been known for centuries.
The ancient Phoenicians, for example, knew that water, wine, or vinegar kept in silver vessels stayed fresh during long sea voyages. However, only recently have scientists discovered how silver does its work.
Silver interrupts a bacteria cell’s ability to form chemical bonds essential to its survival. These bonds produce the cell’s physical structure, so bacteria in the presence of silver literally fall apart.
Cells in humans and other animals have thick walls and are not disturbed by silver. Therefore, silver prevents bacterial growth but is harmless to humans.
One of the most important uses of silver as a biocide is in hospitals and other healthcare facilities because they grapple with MRSA (Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus), a type of life-threatening Staph germ.
Also known as a ‘super-bug,’ MRSA is resistant to almost all chemical antibiotics, so many hospitals are employing silver-embedded equipment, including surgical tools, catheters, needles, stethoscopes, furniture, door handles, and even paper files.
One of the most promising medical applications is in silver-embedded bandages for burn and wound victims. The silver ions help prevent infection and speed healing because the body doesn’t have to focus its energy on fighting infection.
There is a surge in applications for silver-based biocides in all areas: industrial, commercial, and consumer. The newest trend is the use of nano-silver particles to deliver silver ions.
Mirrors and Coatings
When polished, silver offers nearly perfect reflectivity, which makes it ideal for energy-efficient windows.
While silver-coated mirrors have been around for hundreds of years, the coatings are extremely thin, almost transparent coating of silver on window panes not only reflects the sun's heat but also deflects the rooms' internal heat.
Over 250 million square feet of silver-coated glass are used for domestic windows, and much more is employed for silver-coated polyester sheets for retrofitting windows.
In addition, one of every seven pairs of prescription eyeglasses sold in the U.S. incorporates silver. Silver halide crystals melted into the glass can change light transmission from 96% to 22% in less than 60 seconds and block at least 97% of the sun's ultraviolet rays.
These lenses are very popular as they allow people to move from indoor to outdoor activity and back again without the need to change eyeglasses.
Another use of silver is in paints. Silver ions offer an anti-bacterial shield that keeps the coating germ- and fungus-free, used in healthcare facilities, jails, schools, food and beverage factories, and other places where bacteria growth can be a health hazard.
Solar Energy
Silver paste is in 90 percent of all crystalline silicon photovoltaic cells, the most common type of solar cell. Photovoltaic systems are simple and provide immediate power with no pollution.
Solar thermal power systems use concentrated solar energy Silver generates electricity by reflecting and concentrating solar energy onto collector tubes containing salts, which run generators, which heat the tubes and the nitrate salt inside them to over 1050°F. The scalding hot salt is then piped to boilers, turning water into steam, which drives steam turbines that run electric generators. They generate electricity to power 10,000 homes. (Source: eia.gov)
Water Purification
The benefit of having a silver-ion filter is that it replaces traditional germ-killing methods that employ harsh, sometimes dangerous chemicals such as chlorine and bromine.
Silver ions prevent bacteria and algae buildup; silver is fast becoming part of water purification systems in hospitals, small community water systems, pools, and spas.
Purified water is becoming a scarce commodity in some locations, which is making the silver ion filter a much-needed asset in developed and emerging markets.
Silver Supply and Demand 2011-2019
Sources:
USGS.gov - Silver Statistics and Information
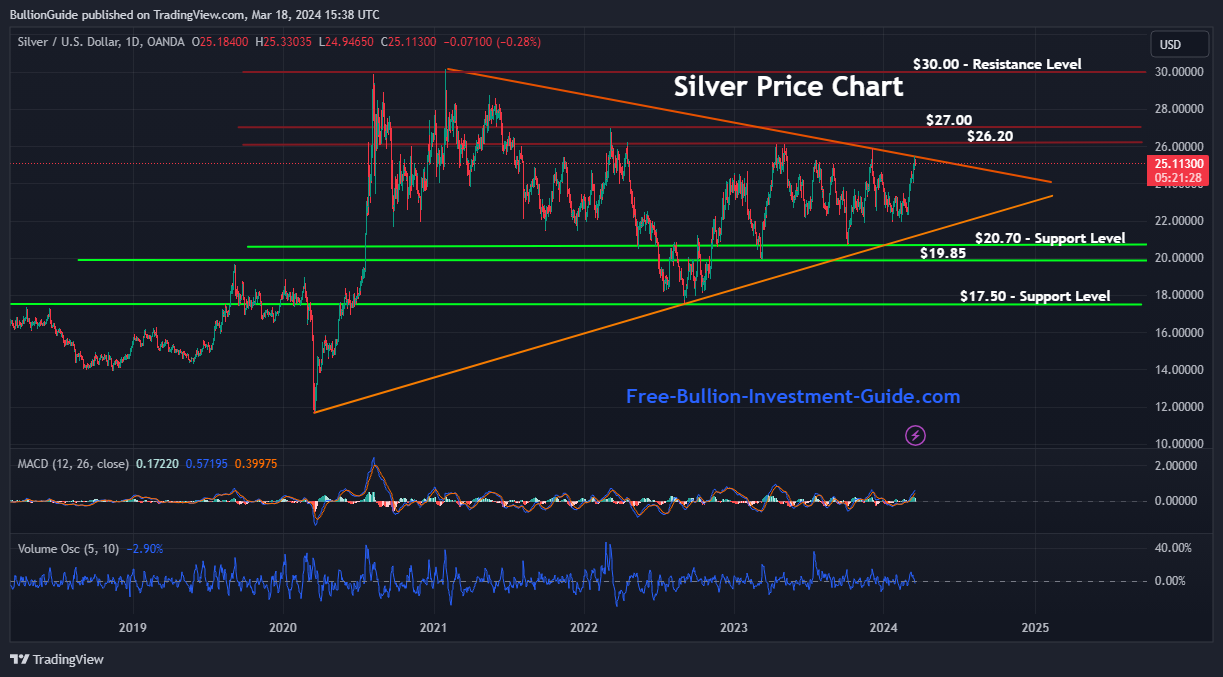
Silver Price Charts (per troy ounce)
➤ Includes:
1) Silver Spot Price - Candlestick Interactive Chart
2) Silver Spot Price - Foreign Currency Charts
3) Silver Spot Price - 20-year (High, Low, Close) Interactive Price Chart
Other pages you may like...
|
|
|
|
|
Free Shipping on Orders Over $100 (US & Canada) |
Silver Supply and Demand 2011- 2019
Free Shipping on Orders $299 & up
SilverGoldBull - 5.0 star Customer Reviews
For Bullion Market News...
|
 | |||||
Free Bullion Investment Guide

Search the Guide
| search engine by freefind | advanced |

Daily
Updated
Updated
Numismatic & Bullion Auctions page
3/21/2024
Updated
03/07/2024
Blog Post
Updated
Update
Update
New Page
Mintage Figures
2023
Mintage Figures
Archangel Raphael
~
The Angel of Healing
Help Us Expand our Audience by forwarding our link
www.free-bullion-investment-guide.com.
Thank You!

March's

pages
Bullion Refiner
Bullion Refiner